| |
|
Carney & Wehofer Family
Genealogy Pages
|
 |
|
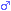 1336 - 1375 (39 years) 1336 - 1375 (39 years)
Generation: 1
| 1. | Edward II 1St Baron Le DESPENSER, Kg, Sir was born on 24 Mar 1335-1336 in Essendine, Rutlandshire, England (son of Sir Edward LE DESPENCER and Anne FERRERS); died on 11 Nov 1375 in Llanbethian, Glamorganshire, Wales; was buried in Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England. Other Events:
- FamilySearch ID: LZ2W-NR3
- _UID: 47C88555836842D7AA6E5FB95358EE6B2142
- MilitaryService: 19 Sep 1356, Poitiers, Vienne, France; Battle of Poitiers
- Title: 1357, England; He became 1st Lord Despenser (Baron Despenser) when he was summoned to Parliament
Notes:
Edward le Despenser, 1st Lord (Baron) le Despenser, so created by writ of summons to Parliament 15 Dec 1357; KG (1361); fought at Battle of Poitiers 1356, Constable of English Army in an unsuccessful invasion of France 1373-74. [Burke's Peerage]
Sir Edward Despenser, KG, b. Essendine 24 Mar 1335/6, d. Llanbethian 11 Nov 1375; m. bef. Dec 1364 Elizabeth de Burghersh (13-9), d. 26 July 1409. [Magna Charta Sureties]
d was present at the Battle of Poitiers. In recognition of his conduct in the French wars, he was summoned to Parliament as a baron in 1357. At the same time, he also became a Knight of the Garter.
He was a friend and patron of Jean Froissart[1] and the eldest brother of Henry le Despenser, Bishop of Norwich.
There is a statue of him on the top of the Holy Trinity Chantry Chapel in Tewkesbury Abbey, renowned as the "KNEELING KNIGHT".
Edward married Elizabeth Burghersh, daughter of Bartholomew Burghersh, 2nd Baron Burghersh.
They had the following children:
- Margaret Despencer (died 3 November 1415), married Robert de Ferrers, 4th Baron Ferrers of Chartley
- Elizabeth Despenser (died 10 or 11 April 1408) married
(1) John FitzAlan, 2nd Baron Arundel (30 November 1364 ? 14 August 1390)
(2) William Zouche, 3rd Baron Zouche
- Thomas Despencer, 1st Earl of Gloucester (22 September 1373 ? 13 January 1400), married Constance of York
- Hugh Despencer
- Cicely Despencer
- Anne Despencer (died 30 October 1426) married (1) Hugh de Hastings and (2) Thomas de Morley, 4th Baron Morley
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_le_Despencer%2C_1st_Baron_le_Despencer
Edward married Elizabeth De BURGHERSH on 2 Aug 1354. Elizabeth (daughter of Bartholomew 4Th Baron De BURGHERSH, Kg, Sir and Cicely De WEYLAND) was born in 1342 in Ewyas Lacy, Herefordshire, England; died on 26 Jul 1409. [Group Sheet] [Family Chart]
Children:
- Phillip le DESPENSER was born about 1357 in Gloucestershire, England; and died.
- Anne Le DESPENSER was born about 1360 in Llanbethian, Glamorganshire, Wales; died between 30 and 31 Oct 1426 in Hockering, Mitford, Norfolk, England; was buried in Austin Friars, Norwich, Norfolk, England.
- Margaret Le DESPENSER was born about 1365 in Ewyas Lacy, Herefordshire, England; died on 3 Nov 1415 in Bugbrooke, Northampton, Northamptonshire, England; was buried in Abbey Of Merevale, Warwickshire, England.
- Elizabeth Le DESPENSER was born about 1367 in Essendine, Rutlandshire, England; died between 10 and 11 Apr 1408 in Harringworth, Northamptonshire, England; was buried in Tewkesbury Abbey, Gloucestershire, England.
- Cicely DESPENSER was born in 1370 in Essendine, Rutland, England; died on 11 Apr 1408 in Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England.
- Thomas Le DESPENSER, Earl Of Gloucester, Kg was born on 22 Sep 1373 in Essendine, Rutlandshire, England; died on 13 Jan 1399-1400 in Beheaded At Bristol, Gloucestershire, England; was buried in Tewkesbury Abbey, Gloucestershire, England.
- Hugh DESPENSER was born about 1375 in Essendine, Rutland, England; died in 1411 in London, , Middlesex, England.
|
Generation: 2
| 2. | Sir Edward LE DESPENCER was born in Oct 1310 in Buckland, Buckinghamshire, England (son of Lord Hugh "The Younger" LE DESPENCER and Eleanore (Alianore) De CLARE); died on 30 Sep 1342 in Morlaix, Brittany, France. Other Events:
- FamilySearch ID: LY9N-JV6
- _UID: 86F8DF5D5E484D7489B3924B16E7D41E294C
Notes:
AFN:84ZQ-ZK
Edward married Anne FERRERS. Anne was born in 1337 in Groby, Leicestershire, England; died on 8 Aug 1367 in Yoxall, Staffordshire, England; was buried on 1 Sep 1367 in Yoxall, Staffordshire, England. [Group Sheet] [Family Chart]
|
| 3. | Anne FERRERS was born in 1337 in Groby, Leicestershire, England; died on 8 Aug 1367 in Yoxall, Staffordshire, England; was buried on 1 Sep 1367 in Yoxall, Staffordshire, England. Other Events:
- FamilySearch ID: KT3Y-4SX
Children:
- 1. Edward II 1St Baron Le DESPENSER, Kg, Sir was born on 24 Mar 1335-1336 in Essendine, Rutlandshire, England; died on 11 Nov 1375 in Llanbethian, Glamorganshire, Wales; was buried in Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England.
|
|
Generation: 3
| 4. |  Lord Hugh "The Younger" LE DESPENCER was born in 1287 in Barton, Gloucestershire, England (son of Hugh III "The Elder" Le DESPENCER, Sir/Earl Winchester and Isabel De BEAUCHAMP); died on 24 Nov 1326 in Hereford, Herefordshire, England; was buried in Tewkesbury Abbey, Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England. Lord Hugh "The Younger" LE DESPENCER was born in 1287 in Barton, Gloucestershire, England (son of Hugh III "The Elder" Le DESPENCER, Sir/Earl Winchester and Isabel De BEAUCHAMP); died on 24 Nov 1326 in Hereford, Herefordshire, England; was buried in Tewkesbury Abbey, Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England. Other Events:
- Death: ; The younger Despenser was hung, drawn and quartered at Hereford the following month, November 1326, after his father was hung, beheaded and quartered.
- FamilySearch ID: 9CQ1-X4J
- Name: The Younger
- Occupation: ; 2nd Lord Despenser (29 Jul 1314-10 Oct 1325); King's Chamberlain; Constable of Odiham Castle; Keeper of the castle and town of Dryslwyn and Cantref Mawr, Carmarthenshire; Keeper of the Castle and town of Portchester; Keeper of the Castle, won and barton
- _UID: 09DC8F794CEF4A62A5549114FED7F1B1E9E4
- TitleOfNobility: Between 1314 and 1326; Lord of Glamorgan
- Execution: 24 Nov 1326, Hereford, Herfordshire, England; Hanged, drawn and quartered
Notes:
He and his father were banished in 1321 but returned in 1322 after barons were defeated at Boroughbridge; he and his father were the real rulers of England until they were executed in 1326 after the invasion of Queen Isabella. See J.C. Davies,
"Baronial Opposition to Edward II" (1918, repr. 1967). COLUMBIA ENCYCLOPAEDIA. from materials provided by Debrett's: "Having gone to parts beyond seas without licence, contrary to the King's inhibition, in Jan. 1309/10, his lands and goods were
taken into the King's hand for a time. Chamberlain towards the end of this year, he being then an adherent of the Earl of Lancaster. Appointed Constable of Odiham Castlel, 1 Nov. 1317: this he had to resign next year. Appointed Keeper of the
castle and town of Dryslwyn, and Cantref Mawr, co. Carmarthen, 18 Nov. 1317; this he had to resign, 14 Sept 1318, but it was regranted to him with the assent of the Par. of York, 21 Nov. following. At this Parl. he was re-appointed Chamberlain.
He was appointed a Constable of Odiham Castle, 22 Feb. 1319/20 to 21 June (or July 9) 1321. He accompanied the King to France in June 1320. Keeper of the castle, town, and barton of Bristol, 1 Oct 1320 to 10 May 1321. On 19 Augl. 1321 he was disinherited and exiled, as mentioned above, his lands being taken into the King's hand, 15 Sep. 1321. He took refuge in the Cinque Ports, and, engaging in piracy, with the King's connivance, did considerable damage. He had letters of safe
conduct for a year, 8 Dec. 1321, and of protection, 9 Jan. 1321/2. In Mar. following he accompanied the King against the contrariants, and is said to have urged him, when at Burton-on-Trent (10 Mar.), not to prosecute war. After the battle of
Boroughbridge, he received large grants of lands forfeited by the rebels. He was appointed Keeper of the castle, town, and barton of Bristol during the King's pleasure, 3 May 1322, and for life, 1 June 1325. Appointed Keepr of the castles,
manors, and lands of Brecknock, Hay, Cantref Selyf, Talgarth, Blaen Llyfni, and Pencelly, co. Brecon, and Huntington, co. Hereford, 10 July 1322. He received a pardon for all his debts at the Exchequer and in the Wardrobe, 5 June 1323. In
1324 he complained to the Pope that he was threatened by magical and secret dealings: but the Pope could only advise him to tur to God with his whole heart and to make a good confession. He was appoitned a commissioner to make peace with the Scots, 8 Nov. 1324. On 1 June 1325 he received a pardon for the acts of piracy which he had committed in 1321. He was sum. for Military Service from 30 June (1314) 7 Edw. II to 1 May (1325) 18 Edw. II, and to Parl. from 29 July (1314) 8 Edw.
II to 10 Oct (1325) 19 Edw. II, by writes directed Hugoni le Despenser juniori, whereby he is held to have become LORD LE DESPENSER. He was taken to Hereford, tried -- without being allowed to speak in his own defence -- condemned to death as a traitor, and hanged on a gallows 50 feet high, 24 Nov. 1326. His head was set up on London Bridge, 4 Dec, and his quarters in four different places. Some years afterwards, his bones were collected, and bur. in Tewkesbury Abbey. On his death all his honors were forfeited, the sentence of "Exile" passed on him in 1321 being re-affirmed in Parl. I Edw. III. The Queen obtained his movables, plate, and jeweles, 8 Jan. 1326/7.SOURCE: Dict. Nat. Bio. 863-5; Ligon Book p.196-859; Amer. Royal Desc. p.449;
Fosters p. 121; The Royal Line (Adamic Genealogy) March 1980, Albert F. Schmuhl
Despenser, Hugh le, English nobleman, son of Hugh le Despenser. A supporter of the king against the barons, he fought under Edward I, for whom he secured a papal release from an oath to refrain from excessive taxation. When the barons forced Edward's son and successor, Edward II, to banish his favorite, Piers Gaveston, le Despenser supported Gaveston and in 1312 succeeded him as the royal favorite. Edward II made him earl of Winchester in 1322, and le Despenser, together with his son, Hugh, acquired vast wealth. The barons established a coalition to challenge Edward II and le Despenser, and open warfare broke out between the king and the barons. At the battle of Boroughbridge in 1322, the king's forces defeated the coalition. The elder le Despenser became virtual ruler of England, instituted several important administrative reforms, and concluded peace with Scotland in 1323. In 1326 Isabella, queen consort of England, formed an alliance with the barons against Edward and the le Despensers in favor of Edward's and Isabella's son, young Prince Edward. In a general uprising, the forces of Edward II were defeated and both father and son le Despenser were hanged.
Hugh married Eleanore (Alianore) De CLARE on 1 May 1306 in Westminister, London, Middlesex, England. Eleanore (daughter of Gilbert I "The Red Earl" De CLARE, Sir Knight/9Th Earl/Gloucester and Princess Joan PLANTAGENET, of Acre) was born on 3 Oct 1292 in Caerphilly Castle, Caerphilly, Glamorganshire, Wales; died on 30 Jun 1337 in Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England. [Group Sheet] [Family Chart]
|
| 5. |  Eleanore (Alianore) De CLARE was born on 3 Oct 1292 in Caerphilly Castle, Caerphilly, Glamorganshire, Wales (daughter of Gilbert I "The Red Earl" De CLARE, Sir Knight/9Th Earl/Gloucester and Princess Joan PLANTAGENET, of Acre); died on 30 Jun 1337 in Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England. Eleanore (Alianore) De CLARE was born on 3 Oct 1292 in Caerphilly Castle, Caerphilly, Glamorganshire, Wales (daughter of Gilbert I "The Red Earl" De CLARE, Sir Knight/9Th Earl/Gloucester and Princess Joan PLANTAGENET, of Acre); died on 30 Jun 1337 in Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England. Other Events:
- FamilySearch ID: LD93-WKS
- _UID: 719E2F8F9A5B4F74A54B9A6FF3BED9373F5D
Notes:
SOURCE: Nat. Dic. of Bio.; Complete Peerage vol III; Banks Dormant Peerage vol
III; The Royal Daughter of England Eng120 p.182-3; The Royal Line (Adamic
Genealogy) March 1980, Albert F. Schedule was committed to the Tower, 17 Nov. 1326 (before the execution of her husband). Her lands were restored to her, 22 Apr. 1328, and the King took her homage and fealty therefor, 11 May following. Before Jan. 1328/9 she was abducted from
Hanley Castle by Sir William La Zouche de Mortimer, of Ashby, co. Leicester, who (subsequently) married her. Soon afterwards this William, accompanied by her, was besieging her castle of Caerphilly, and orders for their arrest issued, 5 Feb.
1328/9. She was imprisoned in the Tower and then in Devizes Castle, and though ordered to be released by the King and his Council did not regain her liberty till after 6 Jan 1329/30. [on the same day she was kidnapped from Hanley Castle by
Zouche] John de Grey [of Rotherfield] claiming her as his wife, obtained a commission of oyer and terminer. He was still claiming her as late as May 1333, having in the interval pursued her, with little success, through various ecclesiastical
courts, the Pope having been appealed to a at least three times. In Jan. 1331/2 he had hot words with his rival before the King and the council. "Et apres les choudes paroles si mist le dit monsire Johan mayn au cotel et treit en partie, mes
ne mie tut hors de gayne." For this he was imprisoned, and his lands taken into the King's hand, for a couple of months. ---------------------------- She was charged with having stolen from the Tower jewels and treasure of great value [these
were probably her late husband's, his wardrobe having been there]. In the petition she stated that Roger de Mortimer, late Earl of March, had said openly tht she would not be released till she and her husband had surrendered to the King her
lands of Glamorgan and Morgannoc, and the manors of Hanley and Tewkesbury, which Roger coveted. Accordingly, by indenture dated 30 Dec. 3 Edw. III, they granted all these lands to the King, the same to be restored to the premises for a fine of L10,000 in one day, and they were pardoned 22 Feb. following. On 19 Jan. 1330/1, after Mortimer had been hanged, they recovered the premises for a fine fo L10,000, reduced 3 days afterwards to L5,000. On 13 Oct. 1335 they were pardoned a futher 2,000 marks, but the fine was not paid in full during their lives. She was committed to the Tower, 17 Nov. 1326 (before the execution of her husband).
Children:
- Hugh LE DESPENCER was born about 1308 in Stoke, Gloucestershire, England; died on 8 Feb 1348-1349; was buried in High Altar, Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England.
- 2. Sir Edward LE DESPENCER was born in Oct 1310 in Buckland, Buckinghamshire, England; died on 30 Sep 1342 in Morlaix, Brittany, France.
- Isabel LE DESPENCER was born about 1312 in Gloucester, Gloucestershire, England; died on 11 Jan 1371 in Arundel, Sussex, England; was buried after 11 Jan 1371 in Tewkesbury, Tewkesbury Borough, Gloucestershire, England.
- Joan DESPENCER was born about 1316 in Stoke, Gloucestershire, England; died on 26 Apr 1394.
- Eleanor LE DESPENSER was born about 1319; died in 1351 in Sempringham with Pointon and Birthorpe, Lincolnshire, England.
- Gilbert DESPENCER was born about 1320 in Of Mowbray, Leicestershire, England; and died.
- Elizabeth Le DESPENCER was born in 1322 in Stoke, Gloucestershire, England; died on 13 Jun 1389; was buried in St. Botulphes.
- Margaret DESPENCER was born in Aug 1323 in Stoke, Gloucestershire, England; died in 1337 in Whatton Priory.
|
|
Generation: 4
| 8. | Hugh III "The Elder" Le DESPENCER, Sir/Earl Winchester was born on 1 Mar 1260 in Of, Winchester, Hampshire, England Or Louch (son of Sir Knight Hugh LE DESPENCER and Aline (Aliva) (Alice) BASSETT, Countess Of Norfolk); died on 27 Oct 1326 in Bristol, Gloucestershire, Eng (Hanged, Drawn And Quartered); was buried on 24 Nov 1326 in Tewkesbury Abbey, Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England. Other Events:
- Cause of Death: ; hung, beheaded and dismembered
- Death: ; He was hanged in his armour and then beheaded. His body was cut into pieces for the dogs, his head sent to Winchester and put on display there.
- FamilySearch ID: LB55-134
- Name: Earl OF WINCHESTER
- Name: Hugh DESPENSER
- Name: The Elder
- _UID: 70BF73754B6048E793411E243CC48BA335BB
- Knighted: 1306, with Edward II
- Owned: 1314, Cardiff, Wales
Notes:
DEATH: CAUS Executed via hanging, drawn & quartered.
Hugh Dispenser, senior, so called to distinguish him from his son, who bore the designation of Hugh Despencer, junior, both so well known in history as the favourites of the unfortunate Edward II. Of Hugh, senior, we shall first treat, although as father and son ran almost the same course at the same time and shared a similar fate, it is not easy to sever their deeds. Hugh Despencer paid a fine of 2,000 marks to the king, in the 15th of Edward I, for marrying without license Isabel, dau. of William de Beauchamp, Earl of Warwick, and widow of Patrick Chaworth; by this lady he had an only son, the too celebrated Hugh Dispenser, jun.
In the 22nd of the same reign, he was made governor of Odiham Castle, co. Southampton, and the same year had summons to attend the king at Portsmouth prepared with horse and arms for an expedition into Gascony. In two years afterwards he was at the battle of Dunbar in Scotland, where the English triumphed, and the next year he was one of the commissioners accredited to treat of peace between the English monarch and the kings of the Romans and of France. In the 26th and 28th years of Edward, he was again engaged in the wars of Scotland and was sent by his sovereign, with the Earl of Lincoln, to the papal court to complain of the Scots, and to entreat that his holiness would no longer favour them as they had abused his confidence by falsehoods. To the very close of King Edward I's reign, his lordship seems to have enjoyed the favour of that great prince, and had summons to parliament from him from 23 June, 1295, to 14 March, 13222, but it was after the accession of Edward's unhappy son, the second of that name, that the Spencers attained that extraordinary eminence from which, with their feeble-minded master, they were eventually hurled into the gulf of irretrievable ruin.
In the first years of Edward II's reign, we find the father and son still engaged in the Scottish wars. In the 14th year, the king hearing of great animosities between the younger Spencer and Humphrey de Bohun, Earl of Hereford and Essex, and learning that they were collecting their followers in order to come to open combat, interfered and strictly commanded Lord Hereford to forebear. About the same time a dispute arising between the Earl of Hereford and John de Mowbray regarding some lands in Wales, young Spencer seized possession of the estate and kept it from both the litigants. This conduct and similar proceedings on the part of the elder Spencer exciting the indignation of the barons, they formed a league against the favourites and, placing the king's cousin, Thomas Plantagenet, Earl of Lancaster, at their head, they marched with banners flying from Sherburne to St. Alban's, whence they despatched the bishops of Salisbury, Hereford, and Chichester to the king with a demand that they Spencers should be banish, to which mission the king, however, giving an imperious reply in the negative, the irritated nobles continued their route to London when Edward, at the instance of the queen, acquiesced, whereupon the barons summoned a parliament in which the Spencers were banished from England and the sentence was proclaimed in Westminster Hall. To this decision, Hugh the elder submitted and retired, but Hugh the younger lurked in divers places, sometimes on land, and sometimes at sea, and was fortunate enough to capture, during his exile, two vessels near Sandwich, laden with merchandise to the value of D40,000, after which, being recalled by the king, an army was raise which encountered and defeated the baronial forces at Boroughbridge, in Yorkshire. In this action, wherein numbers were slain, the Earl of Lancaster was taken prisoner, was carried to his own castle at Pontefract, and there, after a summary trial (the elder Spencer being one of his judges), beheaded.
The Spencers now became more powerful than ever and the elder was created Earl of Winchester, the king loading him with grants of forfeited estates. He was about the same time constituted warden of the king's forests on the south of Trent. Young Spencer obtained, like his father, immense grants from the lands forfeited after the battle of Boroughbridge, but not satisfied with those, and they were incredibly numerous, he extorted by force whatsoever he please. Amongst other acts of lawless oppression, it is related that he seized upon the person of Elizabeth Comyn, a great heiress, the wife of Richard Talbot, in her house at Kennington, in Surrey, and detained her for twelve months in prison until her compelled her to assign to him the manor of Painswike, in Gloucestershire, and the castle and manor of Goderich, in the marches of Wales, but this ill-obtained and ill-exercised power was not formed for permanent endurance and a brief space only was necessary to bring to to a termination.
The queen and the young prince, who had fled to France and had been proclaimed traitors through the influence of the Spencers, ascertaining the feelings of the people, ventured to return and landed at Harwich with the noblemen and persons of eminence who had been exiled after the defeat at Boroughbridge, raised the royal standard and soon found themselves at the head of a considerable force, when, marching upon Bristol where the king and his favourites then were, they were received in that city with acclamation, and the elder Spencer being seized (although in his ninetieth year), was brought in chains before the prince and the barons, and received judgment of death, which was accordingly executed by hanging the culprit upon a gallows in the sight of the king and of his son upon St. Dennis's day, in October, 1326. It is said by some writers that the body was then cut to pieces and given to the dogs. Young Spencer, with the king, effected his escape, but they were both soon afterwards taken and delivered to the queen, when the unfortunate monarch was consigned to Berkeley Castle where he was basely murdered in 1327. Hugh Spencer, the younger, it appears, was impeached before parliament and received sentence "to be drawn upon a hurdle with trumps and trumpets throughout all the city of Hereford," and there to be hanged and quartered, which sentence was executed on a gallows 50 feet high, upon St. Andrew's eve anno 1326 (20 Edward II), Thus terminated the career of two of the most celebrated royal favourites in the annals of England. The younger Hugh, as well as his father, was a peer of the realm, having been summoned to parliament as a baron from 29 July, 1314, to 10 October, 1325, but the Baronies of Spencer and the Earldom of Winchester expired under the attainders of the father and son. [Sir Bernard Burke, Dormant, Abeyant, Forfeited, and Extinct Peerages, Burke's Peerage, Ltd., London, 1883, p. 166, Despencer, Earl of Winchester]
*******
Hugh le Despenser ("The Elder Despenser"), 1st Lord (Baron) le Despenser of the 1295 Creation and 1st and last Earl of Winchester, so created 10 May 1322; called to Parliament by writ 24 June 1295, thus being deemed to have been created a baron; sole person of rank to take Edward II's part in the quarrel with his nobles over the notorious royal favourite Piers Gaveston, whom Edward was eventually induced to banish; later represented Edward in negotiating a treaty with his nobles at the time of Gaveston's murder by them in 1312; at Battle of Bannockburn 1314; banished from court by the machinations of his enemies Feb 1314/15; disinherited and exiled in perpetuity Aug 1321, through malign influence over Edward; this judgement reversed Jan 1321/2 and May 1322; and after Edward II had fled to Wales was convicted as a traitor and hanged 27 Oct 1326, when all his honours were forfeited. [Burke's Peerage]
-------------------------------------------------------------
Hugh and his son were favorites of King Edward II (a weak king) and helped him throw off the mastery of Thomas, Earl of Lancaster. Edward's reliance on the Despencer's drew the ire of his wife Isabel. She had become the mistress of Roger de Mortimer while on a diplomatic mission to France. In September 1326 the couple invaded England, executed the Despencers, and deposed Edward II in favor of his son, Edward III. See Encyclopedia Britannica, Edward II.
*********
Hugh married Isabel De BEAUCHAMP before 1286. Isabel (daughter of Earl William DE BEAUCHAMP, of Warwick and Maud FITZJOHN) was born in 1255 in Warwick, Warwickshire, England; died on 30 May 1306 in Elmley Castle, Worcestershire, England. [Group Sheet] [Family Chart]
|
| 9. | Isabel De BEAUCHAMP was born in 1255 in Warwick, Warwickshire, England (daughter of Earl William DE BEAUCHAMP, of Warwick and Maud FITZJOHN); died on 30 May 1306 in Elmley Castle, Worcestershire, England. Other Events:
- FamilySearch ID: LB6W-M1K
- _UID: AC427791E77548DB98009A6BEAFDF82E1F0B
Notes:
Isabel m. Peter Chaworth. [Sir Bernard Burke, Dormant and Extinct Peerages, Burke's Peerage, Ltd., London, 1883, p. 30, Beauchamp, Earls of Warwick]
*******
Children:
- Margaret LE DESPENCER and died.
- Isabel Le DESPENCER, Baroness Hastings was born in 1286 in Winchester, Hampshire, England; died on 4 Dec 1334.
- 4. Lord Hugh "The Younger" LE DESPENCER was born in 1287 in Barton, Gloucestershire, England; died on 24 Nov 1326 in Hereford, Herefordshire, England; was buried in Tewkesbury Abbey, Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England.
- Sir Philip LE DESPENCER was born in 1289 in Stoke, Gloucestershire, England; died on 24 Sep 1313.
|
|
| 10. |  Gilbert I "The Red Earl" De CLARE, Sir Knight/9Th Earl/Gloucester was born on 2 Sep 1243 in Christchurch, Hampshire, England (son of Richard De CLARE and Maud De LACY); died on 7 Dec 1295 in Monmouth Castle, Monmouthshire, Wales; was buried on 22 Dec 1295 in Tewkesbury Abbey, Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England. Gilbert I "The Red Earl" De CLARE, Sir Knight/9Th Earl/Gloucester was born on 2 Sep 1243 in Christchurch, Hampshire, England (son of Richard De CLARE and Maud De LACY); died on 7 Dec 1295 in Monmouth Castle, Monmouthshire, Wales; was buried on 22 Dec 1295 in Tewkesbury Abbey, Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England. Other Events:
- FamilySearch ID: LZ1V-JW1
- Name: The Red Earl
- TitleOfNobility: Between 1262 and 1295; 3rd Lord of Glamorgan
- TitleOfNobility: Between 1262 and 1295; 6th Earl of Hertford
- TitleOfNobility: Between 1262 and 1295; 7th Earl of Gloucester
- TitleOfNobility: Between 1262 and 1295; 8th Lord of Cardigan
- TitleOfNobility: Between 1262 and 1295; 9th Lord of Clare
- TitleOfNobility: Between 1262 and 1295; 9th Lord of Tonbridge
- Military: 14 May 1264, Lewes, Sussex, England; Battle of Lewes
Notes:
One of the greatest of the Clares was Gilbert de Clare, 9th earl of Clare, 7th earl of Hertford, and 6th earl of Gloucester (1243-1295), known as the Red Earl. A leader of the barons in the early stages of the Barons' War against King Henry III, he deserted the baronial side in 1265, thus helping to ensure a royal victory at the Battle of Evesham. Two years later he changed sides again, captured London, and forced the king to accept a negotiated settlement. In 1290 he married Joan of Acre, a daughter of Henry's successor, King Edward I.
Source: A Baronial Family in Medievil England: The Clares, 1217-1314, Michael Altschul, The Johns Hopkins Press, Baltimore, 1965. p 94: "Gilbert de Clare, the "Red Earl" of Gloucester and Hertford, was after Simon de Montfort the single most important figure in the later stages of the baronial opposition to Henry III. From his father Earl Richard he inherited not only the great Clare estates and lordships in England, Wales, and Ireland, but also a position of leadership among the magnates of the realm; and he was destined to play an even more decisive role in the civil wars which determined the fate of the struggle between king and baronage than his father had played in the initial stages of the movement for reform." From same p 104, 107-108: "The victory at Lewes [over Henry III, 14 May 1264] marked the high point of Simon de Montfort's fortunes. Ominously, a number of Simon's supporters deserted him, including the Earl of Gloucester. (P) Gilbert's defection proved the decisive factor in the situation. The chroniclers record a long list of grievances, and the chancery records bear at least some of them out. He had become increasingly dissatisfied with Simon's regime and reproached the earl for his supposed autocratic rule. He was jealous of the position the earl's sons held in the government. He quarreled with Simon over the control of royalist castles and manors, and the exchange of prisoners. He objected to the use of foreign knights in important castles and the failure to expel all the aliens from court. His support for Simon had not been unqualified, as the letter written in the winter of 1263-64 had shown. A combination of grievances thus drove him into opposition." From same, p 108-110: "Simon [de Montfort] took [Lord] Edward and Henry [III] with him to the west, and encamped at Hereford until May 24 [1265]. Attempted negotiations proved fruitless, for Gilbert had already worked out a plan with Edward and Roger Mortimer which would seal Simon's fate. On May 28, with the assistance of Thomas de Clare, Earl Gilbert's younger brother, Edward managed an escape. He joined forces with [Roger] Mortimer at Wigmore, and the next day Gilbert joined them in Ludlow. Wykes, perhaps the best informed chronicler of this period, records an important set of cnditions that Earl Gilbert demanded as the price of his support. The earl made Edward swear a solemn oath that, if victorious, he would cause the "good old laws" of the realm to be observed' evil customs would be abolished, aliens banished from the king's council and administration; and the king would rule with the counsel of his faithful subjects. If Wykes' account of the oath is substantially correct, it clearly shows that Gilbert remained firmly attracted to the principles of the Provisions [of Oxford (1258) and Westminster (1259), granted to the barons by Henry III but not much adhered to], however vaguely envisioned and conventionally expressed, and to the xenophobia which the movement engendered. If he withdrew his support from Simon, it was not because he was willing, like his father Earl Richard in 1260, to repudiate the Provisions, but because he felt that Simon did not distinguish between the baronial ideals and his personal ambition. The cause of reform, in short, was not the exclusive prerogative of the earl of Leicester. (P) The military operations are quickly told. Under the leadership of Edward and Earl Gilbert, the royalists gathered at Gloucester, cutting off Simon's retreat across the Severn at that point. Boldly making his way into the march, Simon renewed his alliance with Llywelyn in the middle of June. He then went through Monmouth to the borough of Newport in the Clare lordship of Gwynllwg and attempted to cross over to Bristol, but this plan was foiled when Earl Gilbert destroyed the convoy sent for that purpose. Simon managed to return to Hereford, and tried to join forces with an army led by his son. Edward and Gilbert, however, surprised the younger Simon at Kenilworth in Warwick on August 1, routed his forces, and immediately doubled back to intercept Earl Simon. The earl reached the Worcester manor of Evesham on August 3, but was surrounded by the royalists. The next day battle [of Evesham] was joined. As Simon advanced on a troop led by Roger Mortimer, Earl Gilbert, who commanded the second line, suddenly attacked from the rear. The outcome was less a battle than a slaughter. The only important marcher who fought with Simon, Humphrey de Bohun the younger, was captured and imprisoned at Beeston castle in Cheshire, where he died on October 27. Two other men with marcher affiliations, Henry de Hastings and John fitz John, were also imprisoned. Otherwise the royalists showed no mercy. Simon de Montfort, his son Henry, his loyal friend Peter de Montfort the elder, the justiciar Hugh Despenser and many others were slain. King Henry himself was rescued by Roger Leyburn. The Montfortian experiment was ended. (P) The death of Simon de Montfort did not produce peace. The ferocity with which the royalists had crushed their enemies carried over into a period of widespread seizures of rebel lands and indiscriminate plundering which produced further turmoil and unrest. In addition, the territorial policy adopted by the restored royal government provoked those supporters of Earl Simon still at large into guerilla operations which turned into full-scale warfare and prevented a final pacification of the kingdom until the end of 1267. In this period the actions of Gilbert de Clare again proved decisive. His support for the disinherited rebels was a major factor in the establishment of internal order following the two years of continued civil strife which constituted the aftermath of the battle of Evesham."
From same, p 120-121: "The most striking feature of Gilbert de Clare's role in the later stages of the baronial movement is its consistency. The Red Earl's shifting allegiance was a sign not of vaillation but of independence. He was the moderating force against the extremes of both the royalist and the Montfortian sides. He was attracted to the baronial movement as a whole, but even more than his father Earl Richard, he drew the crucial distinction between its policies and the great earl whose name is inseparably associated with the movement. Earl Gilbert was not convinced that Simon de Montfort's actions were always and indisputably right, and he withdrew his support when he felt that Simon's regime was no better in its way than King Henry's had been. His adherence to the royalists, however, was no less qualified. When two years of continued resistance to the restored government of Henry III produced further social and political unrest, Earl Gilbert's rising proved the decisive factor in restoring unity and tranquillity to the realm. Unlike Earl Richard, Gilbert had not accepted Henry's repudiation of the principles which underlay the Provisions of Oxford and Westminster. His activities, while strongly colored by personal animosities and conditioned by personal interests, nevertheless reveal a continuity of purpose which did much in helping to incorporate those principles into the fabric of the common law and the conduct of monarchy. From same, p 155-156: "On December 7 [1295] he [Gilbert] died at Edmund of Lancaster's castle of Monmouth, and was buried two weeks later at Tewkesbury Abbey. Most of the chroniclers merely noted his death without further comment, although an interpolation in the chronicle of Walter of Guisborough refers, in rather conventional fashion, to the earl's military prowess and staunch defense of his rights. The Red Earl's last years were spent under the shadow of Edward I's domination, and his stormy career ended in dispirited humiliation. Perhaps the soundest judgment is that contained in the otherwise undistinguished Osnay chronicle. In referring to the earl's marriage to Joan of Acre in 1290, the chronicler calls Gilbert the greatest of the magnates of the realm in nobility and eminence, and incomparably the most powerful man in the kingdom -- next to the king. Later events proved that the chronicler's qualification was more significant than he could have realized at the time." From same, p 41-42: "Taken as a whole, the Clare family represents what might be termed one of the most successful joint enterprises in medieval English history. More than two centuries of steady territorial growth raised the family to a position of pre-eminence in the ranks of the higher nobility. The major factors in this development in the twelfth century were undoubtedly royal favor and shrewdly chosen marriages. The Clares prospered from their intimate connections with successive rulers of England, and the male members of the house were rewarded with a series of important fiefs and well-placed ladies. The power and prestige of the family reached their highest level in the thirteenth century and the fortunes of its members help illuminate almost every aspect of the social and political life of the English baronage in this period."
REF: "Falls the Shadow" Sharon Kay Penman: May 1263 the young Earl of Gloucester led an Army west & captured the Bishop of Hereford, the most hated of the foreign advisors to Henry III then left after the expulsion of the de Lusignans. He threw the Bishop into prison, laid siege to the royal castle at Gloucester, where de Montfort assumed command. The army then went north to Bridgenorth, where they coordinated their attack with Llywelyn ap Gruffydd; the twon & castle surrendered. de Montfort then headed south for London, where a panicked Henry took refuge in the Tower. On April 5 1264 the defeat at Northampton by Prince Edward of Simon de Montfort's forces crippled Simon's forces. Northampton defenses had been allowed to decay in the years previous to de Montfort's occupation there, plus the battle was lost due to the treachery of the Prior at St. Andrew's. After the defeat, Edward allowed his army to have their sport on the town, culminating in utter destruction, rapine, murder, etc. of its inhabitants. Some 80 barons & knights were taken prisoner & the rebel army was gutted. The defeat touched off a riot in London on Apr 9, 1264 in which hundreds, mainly Jews, were slain. Sir Hugh le Despenser, Simon's Justicialar & Thomas FitzThomas, Mayor of London, attempted to control the crowds & saved some lives by offering sanctuary in the Tower. FitzThomas then begged Simon to return to London to quell the Londoners' fear. In May 1264 Edward looted lands of Robert de Ferrers, the Earl of Derby, after he lost Tutbury Castle, Derby defected from Simon's support. King Henry meanwhile took Leicester & Nottingham. Simon & Gilbert de Clare attacked Rochester Castle (which surrendered) & besieged the town when Edward approached London so Simon went back to defend it. King Henry & Edward were practicing fierce cruelty by chopping off the nads & feet of all common soldiers captured from de Montfort's army. The Cinque Ports & Dover Castle held fast for Simon, & did not obey Henry & Edward's command for a naval force to attack London. Thwarted, Edward took Gilbert de Clare's Tonbridge Castle. Simon continued to hold London, but is surrounded by Edward & Henry. Gilbert lets his men loose on the Canterbury Jews using as a weak (& unproven) excuse that they were in league with the King. de Clare had a fairly long histroy of intense hatred for Jews. On the eve of the Battle of Lewes, 14 May 1264, after Henry had refused the entreaty of the Bishops of London & Worcester (Walter de Cabntelou) to negotiate, de Clare followed Simon de Montfort's lead & formally renounced all allegiance to King Henry. With Robert de Vere, the Earl of Oxford, de Clare had the most to lose of any of the rebel supporters. In late July, he joined forces with Montfort & Llywelyn ap Gruffydd & put down a rebellion of the Welsh Marcher Lords, including Roger de Mortimer. In October 1264 he was excommunicated by Papal edict along with other Montfort supporters & Simon himself; however, the sentecne of anathema was not practiced by the English Church. Clare had an extremely prickly sense of pride, & held a mixture of rancor toward Montfort's sons & jealosy of Montfort himself, both of his acclaim & his personal popularity with the people. Clare also could have split because of his intense anti-Jewish sentiment & Montfort's refusal to condone pogroms, etc. In November 1264, Clare had the latest of many quarrels with Montfort's son Bran de Montfort, but this one spilled bad blood for the first time over to Gilbert's brother Thomas de Clare too. Before Nov 1264, Montfort awarded his sons several lucrative appointments; when Clare complained he was brushed off by Montfort. Although after Lewes Clare received the lands of John de Warenne, William de Lusignan & Peter de Savoie, but Montfort rejected his demand for the ransom of Richard of Cornwall (despite the Mise of Lewes proclaiming no ransoms to be paid for prisoners from the battle). Montfort called a Parliament January 1265; at this Parliament Montfort had a very public clash with Clare; Clare withdrew to his estates on the Welsh Marches. Clare was harboring Marcher Lords in violation of the government expulsion edict. Clare was grieved at Montfort's unilateral appointment of his son Amaury as treasurer of York & when in late 1264 Montfort arrested the Earl of Derby & threw him into the Tower of London for wanton lawlessness, extortion & plundering of his neighbors. Many lords, while not feeling sorry for Derby, felt this set a dangerous precedent. Lord paid for political transgressions; not criminal ones. By April/May 1265, Simon & Clare had supposedly patched up a peace again, but Clare was only stalling for time in order to free Prince Edward from the custody of Henry de Montfort & Robert de Ros. Edward had again played his cousin Henry for the fool, gradually getting Henry to trust him & allow him more freedom. While Clare made a visit to King Henry to make a false oath of fealty to the King & Simon's government, he engineered Roger de Mortimer's rescue of Edward from Henry de Montfort to Wigmore castle in May 1265. Gilbert almost goes to war with Roger de Mortimer over the lands of Humphrey de Bohun, who died in captivity soon after Evesham (Aug 4 1265). Gilbert was as uneasy in his new alliance with Edward as he had been formerly with Simon; he simmered until April 1267 he siezed London. He held London for two months until he was able to negotiate an amnesty with Henry. His wife (they shared a mutual hatred for one another) tried to warn her uncle King Henry of Gilbert's intention but he did not believe her until it was too late.
Gilbert de Clare, surnamed the Red, 7th Earl of Hertford and 3rd Earl of Gloucester, who, by the king's procurement, m. in 1257, Alice, dau. of Guy, Earl of Angoulme, and niece of the king of France, which monarch bestowed upon the lady a marriage portion of 5,000 marks. This nobleman, who, like his predecessors, was zealous in the cause of the barons, proceeded to London immediately after the defeat sustained by the insurrectionary lords at Northampton (48th Henry III) [1264], in order to rouse the citizens, which, having effected, he received the honour of knighthood from Montfort, Earl of Leicester, at the head of the army at Lewes; of which army, his lordship, with John Fitz-John and William de Montchensi, commanded the second brigade, and having mainly contributed to the victory in which the king and prince became prisoners, while the whole power of the realm fell into the hands of the victors, the earl procured a grant under the great seal of all the lands and possessions lying in England of John de Warren, Earl of Surrey, one of the most faithful adherents of the king, excepting the castles of Riegate and Lewes, to hold during the pleasure of the crown, and he soon after, with some of the principal barons, extorted from the captive monarch a commission authorizing Stephen, then bishop of Chichester, Simon Montford, Earl of Leicester, and himself, to nominate nine persons of "the most faithful, prudent, and most studious of the public weal," as well prelates as others, to manage all things according to the laws and customs of the realm until the consultations at Lewes should terminate. Being jealous, however, of the power of Leicester, the earl soon after abandoned the baronial cause and, having assisted in procuring the liberty of the king and prince, commanded the second brigade of the royal arm at the battle of Evesham, which restored the kingly power to its former lustre. In reward of these eminent services he received a full pardon for himself and his brother Thomas of all prior treasons, and the custody of the castle of Bergavenny during the minority of Maud, wife of Humphrey de Bohun. His lordship veered again though in his allegiance and he does not appear to have been sincerely reconciled to the royal cause until 1270, in which year, demanding from Prince Edward repayment of the expenses he had incurred at the battle of Evesham, with livery of all the castles and lands which his ancestors had possessed and, those demands having been complied with, he thenceforward became a good and loyal subject of the crown. Upon the death of King Henry, the Earl of Hertford and Gloucester was one of the lords who met at the New Temple in London to proclaim Prince Edward, then in the Holy Land, successor to the crown, and so soon as the new monarch returned to England, his lordship was the first to entertain him and his whole retinue with great magnificence for several days at his castle of Tonebruge. In the 13th Edward I [1285], his lordship divorced his wife Alice, the French princess, and in consideration of her illustrious birth, granted for her support during her life, six extensive manors and parks, and he m. in 1289, Joan of Acre, dau. of King Edward I, upon which occasion he gave up the inheritance of his castles and manors, as well in England as i Wales, to his royal father-in-law, to dispose of as he might think proper; which manors, &c., were entailed by the king upon the earl's issue by the said Joane, and in default, upon her heirs and assigns, should she survive the lordship. By this lady he had issue, Gilbert, his successor, Alianore, Margaret, and Elizabeth. His lordship d. in 1295, and the Countess Joan surviving, m. a "plain esquire," called Ralph de Monthermer, clandestinely, without the king, her father's, knowledge, but to which alliance he was reconciled through the intercession of Anthony Beke, the celebrated bishop of Durham, and became eventually much attached to his now son-in-law. [Sir Bernard Burke, Dormant and Extinct Peerages, Burke's Peerage, London, 1883, pp. 119-120, Clare, Lords of Clare, Earls of Hertford, Earls of Gloucester]
----------
Gilbert de Clare, Earl of Gloucester (1243-1295), 8th earl of Gloucester and 9th earl of Clare, was born at Christchurch, Hampshire, on Sept. 2, 1243. He married Alice of Angoulme, niece of king Henry III, succeeded his father in July 1262, and joined the baronial party led by Simon de Montfort. With Simon, Gloucester was at the battle of Lewes in May 1264, when the king himself surrendered to him, and after this victory he was one of the three persons selected to nominate a council. Soon, however, he quarreled with Simon. Leaving London for his lands on the Welsh border he met Prince Edward, afterward king Edward I, at Ludlow, just after his escape from captivity; and contributed largely to the prince's victory at Evesham in August 1265. But this alliance was as transitory as the one with Leicester, Gloucester championed the barons who had surrendered at Kenilworth in November and December 1266, and after putting his demands before the king, secured possession of London (April 1267). The earl quickly made his peace with Henry III and with Prince Edward. Under Edward I he spent several years in fighting in Wales, or on the Welsh border; in 1289 when the barons were asked for a subsidy he replied on their behalf that they would grant nothing until they saw the king in person (nihi prius personaliter viderent in Anglia faciem regis), and in 1291 he was fined and imprisoned on account of levying private war on Humphrey de Bohun, earl of Hereford. Having divorced his wife Alice, he married in 1290 Edward's daughter Joan, or Johanna (d. 1307). The "Red Earl," as he is sometimes called, died at Monmouth on Dec. 7, 1295, leaving, in addition to three daughters, a son, Gilbert, earl of Gloucester, killed at Bannockburn. [Encyclopaedia Britannica, 1961 ed., Vol. 10, p. 434, GLOUCESTER, GILBERT DE CLARE, EARL OF.]
***********
3d Earl of Gloucester and 7th Earl of HertfordOne of the greatest of the Clares was Gilbert de Clare, 9th earl of Clare, 7th earl of Hertford, and 6th earl of Gloucester (1243-95), known as the Red Earl. A leader of the barons in the early stages of the Barons' War against King Henry III, he deserted the baronial side in 1265, thus helping to ensure a royal victory at the Battle of Evesham. Two years later he changed sides again, captured London, and forced the king to accept a negotiated settlement. In 1290 he married Joan of Acre, a daughter of Henry's successor, King Edward I. When Gilbert de Clare, 10th earl of Clare (1291-1314), died childless, the male line of the Clares came to an end. His sister, Elizabeth de Clare (1291?-1360), founded Clare College at the University of Cambridge.
"Clare (family)," Microsoft(R) Encarta(R) 98 Encyclopedia. (c) 1993-1997 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
******
Gilbert married Princess Joan PLANTAGENET, of Acre on 9 May 1290 in Westminster, Middlesex, England. Joan (daughter of King Edward I "Longshanks" PLANTAGENET and Queen Eleanor DE CASTILLE, Queen Consort of England) was born in Apr 1272 in Acre/Akko, Hazafon, Kingdom of Jerusalem; died on 23 Apr 1307 in Clare Castle, Clare, Suffolk, England; was buried on 26 Apr 1307 in Church of Austin Friars Clare, Suffolk, England. [Group Sheet] [Family Chart]
|
| 11. |  Princess Joan PLANTAGENET, of Acre was born in Apr 1272 in Acre/Akko, Hazafon, Kingdom of Jerusalem (daughter of King Edward I "Longshanks" PLANTAGENET and Queen Eleanor DE CASTILLE, Queen Consort of England); died on 23 Apr 1307 in Clare Castle, Clare, Suffolk, England; was buried on 26 Apr 1307 in Church of Austin Friars Clare, Suffolk, England. Princess Joan PLANTAGENET, of Acre was born in Apr 1272 in Acre/Akko, Hazafon, Kingdom of Jerusalem (daughter of King Edward I "Longshanks" PLANTAGENET and Queen Eleanor DE CASTILLE, Queen Consort of England); died on 23 Apr 1307 in Clare Castle, Clare, Suffolk, England; was buried on 26 Apr 1307 in Church of Austin Friars Clare, Suffolk, England. Other Events:
- Affiliation: ; House of Plantagenet
- FamilySearch ID: 9MK6-P6Z
- TitleOfNobility: ; Countess of Gloucester
- TitleOfNobility: ; Countess of Hertford
Notes:
Joan was a remarkably active woman in the dozen years following the Red Earl's death. By the terms of the marriage agreement of 1290, the entire inheritance was off jointly on Gilbert and Joan. This meant that it would not be possible for her father Edward I to grant her only a third of the estates and control the rest himself during the long minority of her son Gilbert. Joan was thus sole mistress of the inheritance, and she controlled it with marked ability. In1297, much to Edward's displeasure, she secretly married another wise obscure knight in her *familia*, Ralph de Monthermer (d. 1325). Ralph was styled earl of Gloucester *jure uxoris* and for the next decade administered the estates with the king's daughter. After Joan's death, his rights to the estates and title lapsed, and he was thenceforth treated as an ordinary baron. His children by Joan of Acre were likewise excluded from the inheritance, and had no future connection with the Clares, aside from a daugher, Mary, who was married in 1307 to Duncan,son and heir of Duncan, earl of Fife, and Joan, the Red Earl's daughter by his first marriage to Alice de Lusignan. Joan of Acre died in April, 1307, but during her tenure of the inheritance important modifications were introduced in its administrative structure. After Isabella de Fortibus, dowager countess of Devon and Aumale (1262 93), Countess Joan stands as perhaps the best example in thirteenth century English historyof the ability of a widow to run the estates and otherwise manage the complex affairs of a great comital house."
Joan of Acre died in April, 1307, but during her tenure of the inheritance of Gloucester important modifications were introduced in its administrative structure. After Isabella de Fortibus, dowager countess of Devon and Aumale (1262-93), Countess Joan stands as perhaps the best example in thirteenth century English history of the ability of a widow to run the estates and otherwise manage the complex affairs of a great comital house."
--- Michael Altschul, *A Baronial Family in Medieval England: The Clares,
1217-1314*, Baltimore MD (Johns Hopkins Press) 1965. p 38-39.
Gilbert de Clare was not young when he married the fiery-spirited, sloe-eyed Joanna and took her to live at his country retreat in Clerkenwell not far from the Tower, where the king and queen were again in residence. She left for her new home with great fanfare, laden with royal gifts. After being a widow a year, she secretly married a completely unknown squire in her husbands retinue, Ralph de Monthermer. Through this marriage he became possessed in his own right of the earldoms of Gloucester & Hertford. The fact that a royal princess had dared to marry this obscure fellow became a cause celebr which for a time separated her from the affection of her father. It proved to be a marriage, however, leading ultimately to a firm friendship between the new son-in-law and Edward.
*********
Children:
- Richard DE CLARE and died.
- Gilbert DE CLARE, 8th Earl of Gloucester was born on 10 May 1291 in Clare, Suffolk, England; died on 24 Jun 1314 in Bannockburn, Stirlingshire, Scotland; was buried in 1314 in St Mary The Virgin's Church, Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England.
- 5. Eleanore (Alianore) De CLARE was born on 3 Oct 1292 in Caerphilly Castle, Caerphilly, Glamorganshire, Wales; died on 30 Jun 1337 in Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England.
- Margaret DE CLARE was born on 12 Oct 1293 in Tonbridge Castle, Tonbridge, Kent, England; died on 9 Apr 1342 in Chebsey, Staffordshire, England; was buried on 13 Apr 1342 in Tonbridge Priory, Tonbridge, Kent, England.
- Elizabeth De CLARE, Baroness D'amory was born on 16 Sep 1295 in Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England; was christened in 1295 in Tewkesbury, Gloucestershire, England; died on 4 Nov 1360 in Alton Castle, Alton, Staffordshire, England; was buried after 4 Nov 1360 in Minoresses Convent, Aldgate, London, England.
|
|
|
|
|